Kiel Trade and Tariffs Monitor
KITE Scenario Analytics
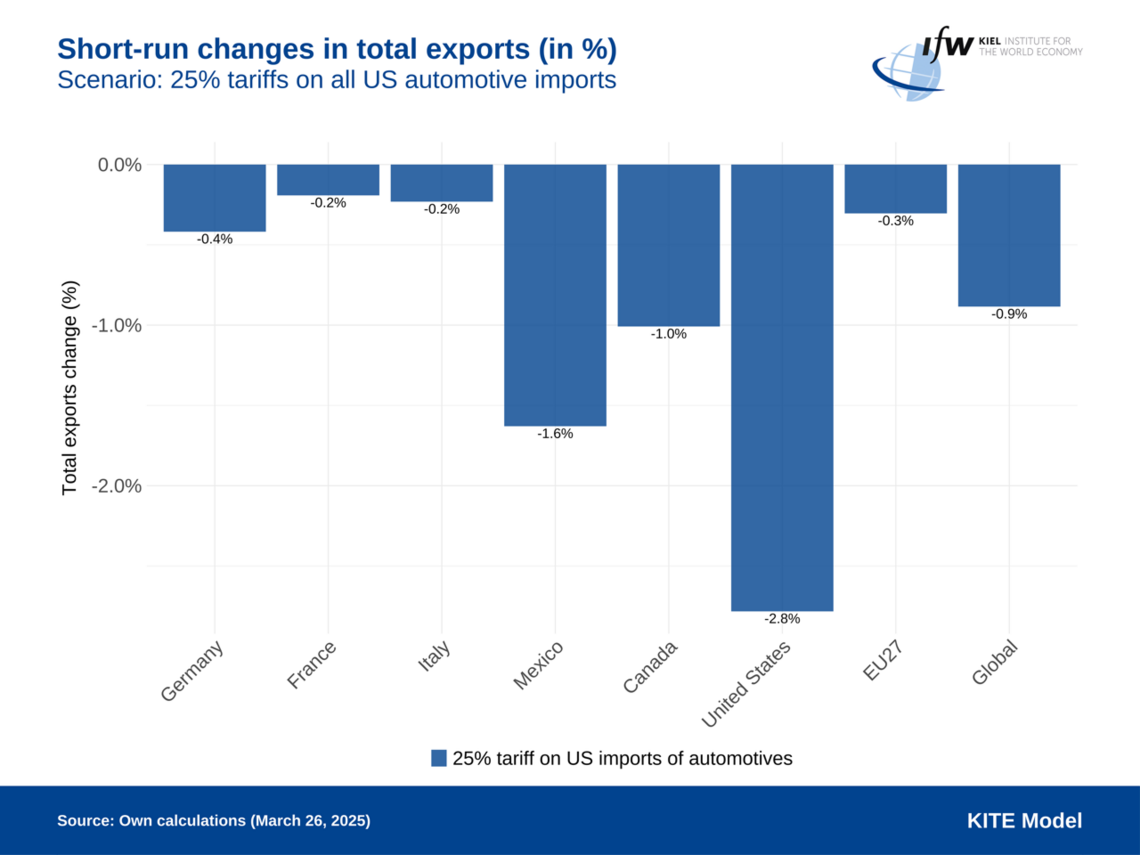
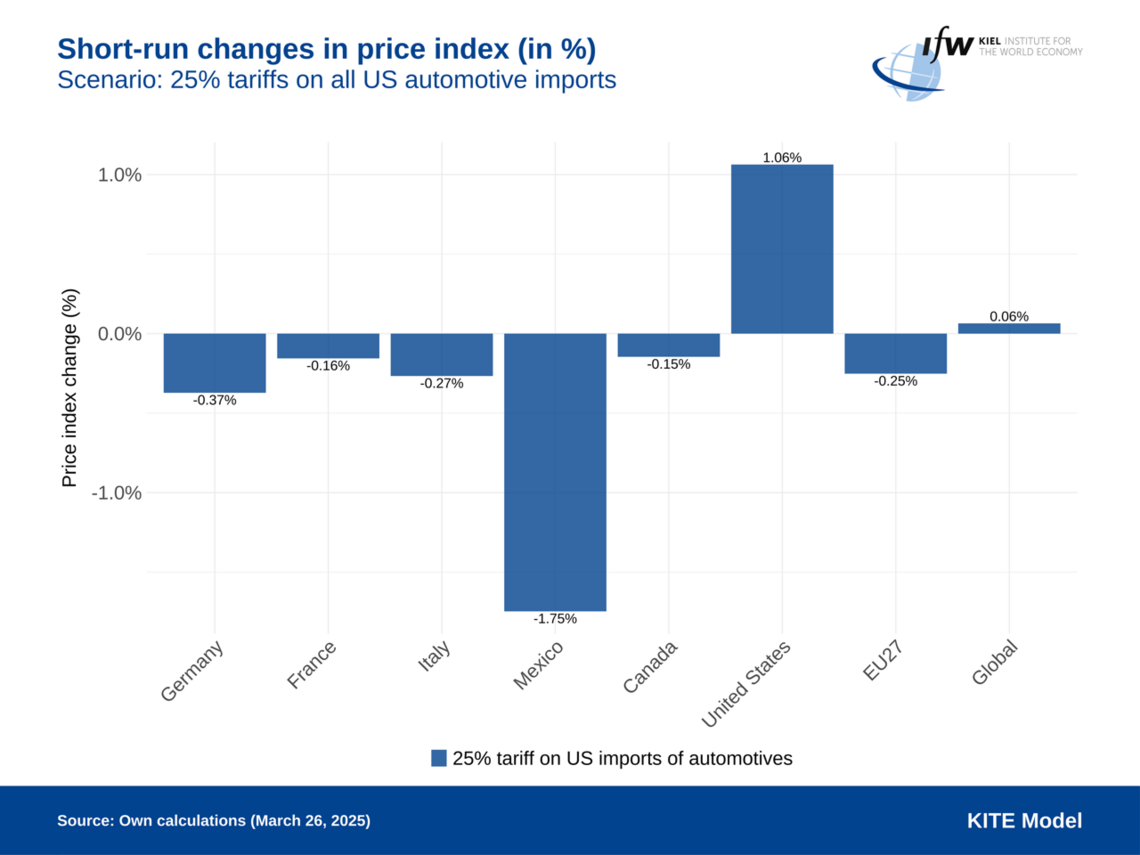
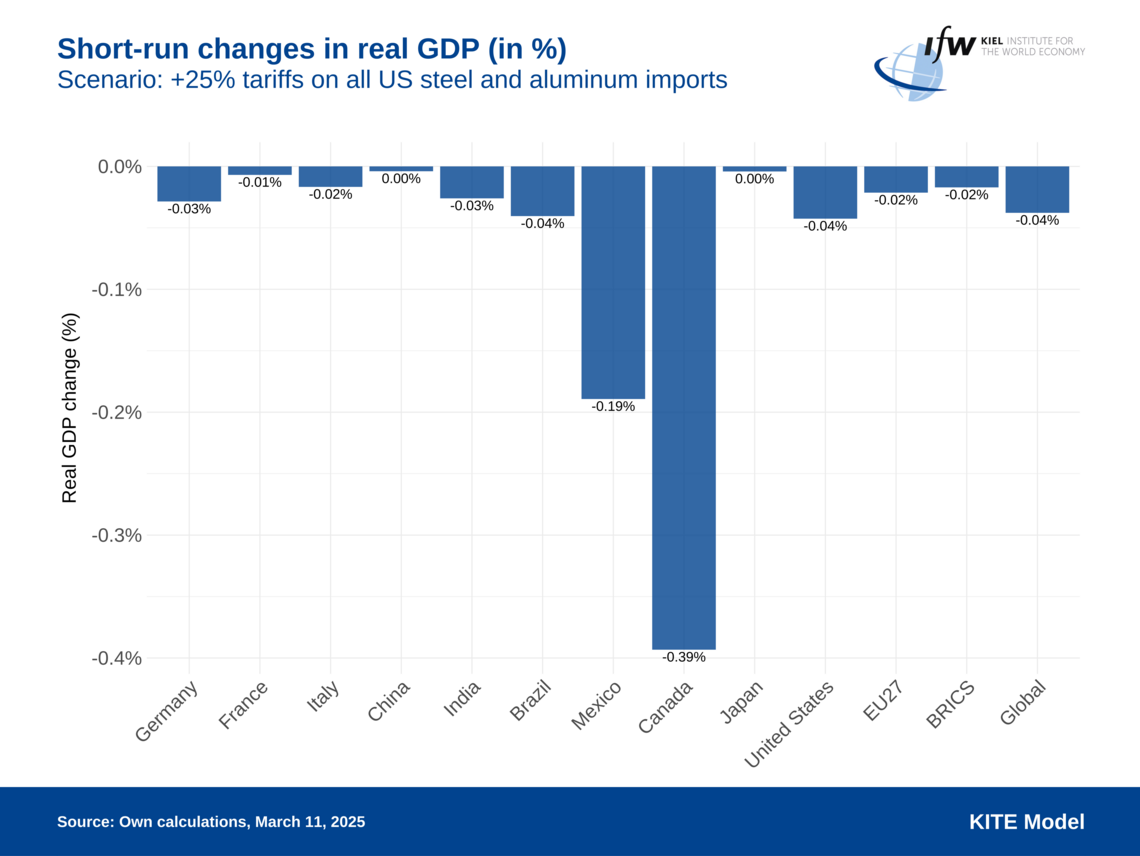
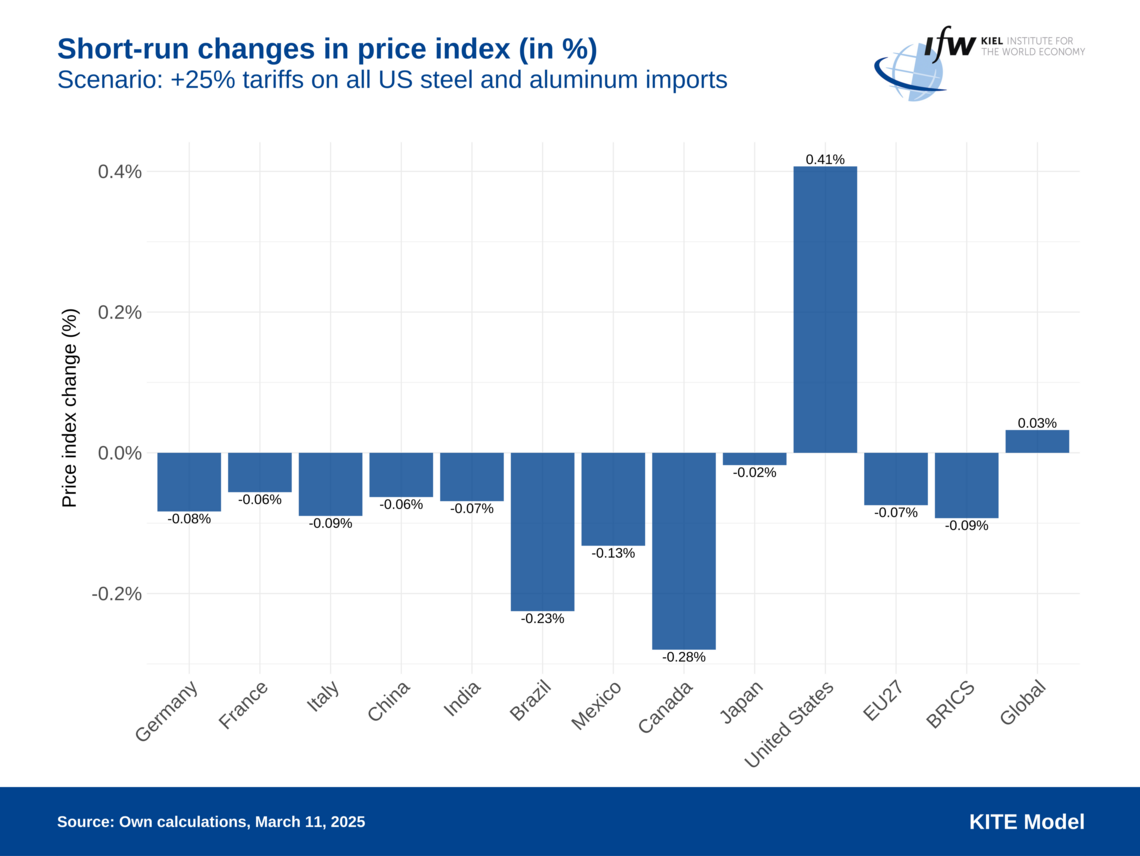
The Kiel Trade and Tariffs Monitor offers in-depth analyses, simulations, and commentaries on the economic impacts of tariffs and trade conflicts. Utilizing the KITE model, the we evaluate scenarios such as the effects of U.S. tariffs on European goods, potential EU countermeasures, and the broader consequences of escalating trade tensions on global economies. To support informed discussions on trade policies, the platform provides access to the raw data used in these analyses, providing structured data of newly announced tariffs. The research is continually updated to reflect current developments, ensuring relevance and accuracy.
More information
News
Tariff Data Download
Access the “tariff deltas,” representing changes in tariffs since January 2025, in CSV format. Detailed information on data structure and sources is available in the accompanying documentation. The files are named "Tariff Deltas [imposing country] - [target country].csv".
Tariff Deltas CAN USA
Tariff Deltas CHN USA
Tariff Deltas USA CAN
Tariff Deltas USA CHN
Tariff Deltas USA erga omnes (EO)
Tariff Deltas USA erga omnes (EO) 02042025
Tariff Deltas EO USA 02042025
Tariff Deltas USA MEX
Tariff Deltas EU USA
Documentation